Chip seal is a surface treatment where pavement or aggregate is sprayed with an emulsified asphalt and immediately covered with aggregate and rolled in place. Multiple layers may be placed and various binder and aggregate types can be used to address specific distress modes or traffic situations.
There are several types of chip seals in use today. They include the following: •
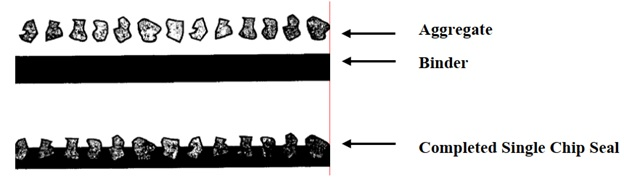
- Single Chip Seal: A single chip seal is an application of binder followed by an aggregate. This is used as a pavement preservation treatment and provides a new skid-resistant wearing surface, arrests raveling, and seals minor cracks. Figure 1 illustrates this type of chip seal application
Figure 1: Single Chip Seal
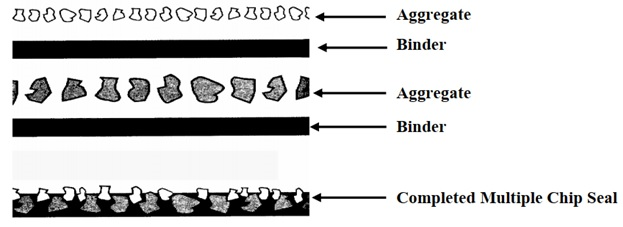
Double Chip Seal: A double chip seal is a built-up seal coat consisting of multiple applications of an asphalt emulsion binder and aggregate. A double chip seal consists of a spray application of binder, spreading a layer of aggregate, rolling the aggregate for embedment, applying an additional application of binder, spreading another layer of aggregate (approximately half the average least dimension of the base layer aggregate), and final rolling.
Sweeping should be done between applications. This process may be repeated, as necessary, to build up a pavement’s edges. Double chip seals are used where a harder-wearing and longer-lasting surface treatment is needed. Figure 2 illustrates a double chip seal application.
Figure 2: Double Chip Seal
The dimensions of the aggregates used in chip seal are 1/4 to 1/2 inch, and usually 1.5 to 1.8 kg of emulsion bitumen and 16 to 18 kg of aggregate are needed per m2 of surface. Cationic emulsion bitumen CRS-1 is also used for this purpose.